| projection |
NSIDC Sea Ice Polar Stereographic North. EPSG:3413
|
| tools |
Python libraries: geopandas, cartopy and matplotlib; along with QGIS
|
| data |
Sentinel-2 acquisition from 19 September 2022 (ESA Copernicus, 2022)
|
| comments |
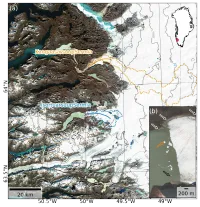
Figure 1 from my paper published in JGlac on Terminus thinning at Isortuarsuup Sermia. With hindsight, the decision to plot a hillshade the illumination azimuth and elevation equal to the solar position at the time the Sentinel-2 scene was acquired was perhaps unneccessary and renders the Satellite Image slightly less crisp and clear. Both glacier labels should be larger
|
| date |
01/01/2024
|